To further improve mRNA stability and translation efficiency, Elonova applies advanced 3′-end modification strategies.
Using poly(U) polymerase–mediated incorporation, modified uridine analogs such as 2′-O-methyl-uridine or pseudouridine can be enzymatically added to the poly(A) tail, enhancing resistance to exonuclease degradation and reducing innate immune activation.
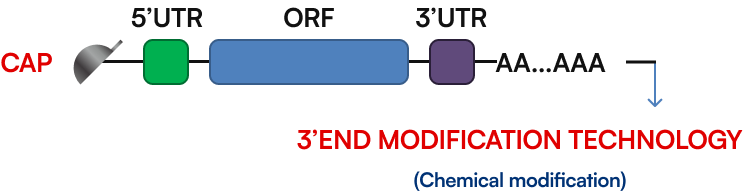
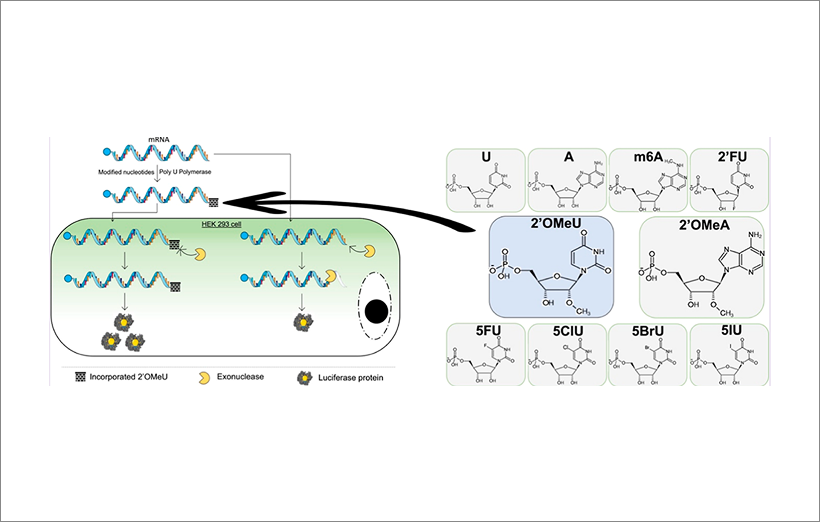
In parallel, a non-enzymatic chemical conjugation approach enables site-specific attachment of modified nucleotides or small molecules at the 3′ terminus, providing flexible control over mRNA stability, localization, and translational behavior.
Together, these complementary methods allow precise and tunable 3′-end engineering to produce more stable, translation-efficient, and immunologically balanced mRNAs for therapeutic and research applications.